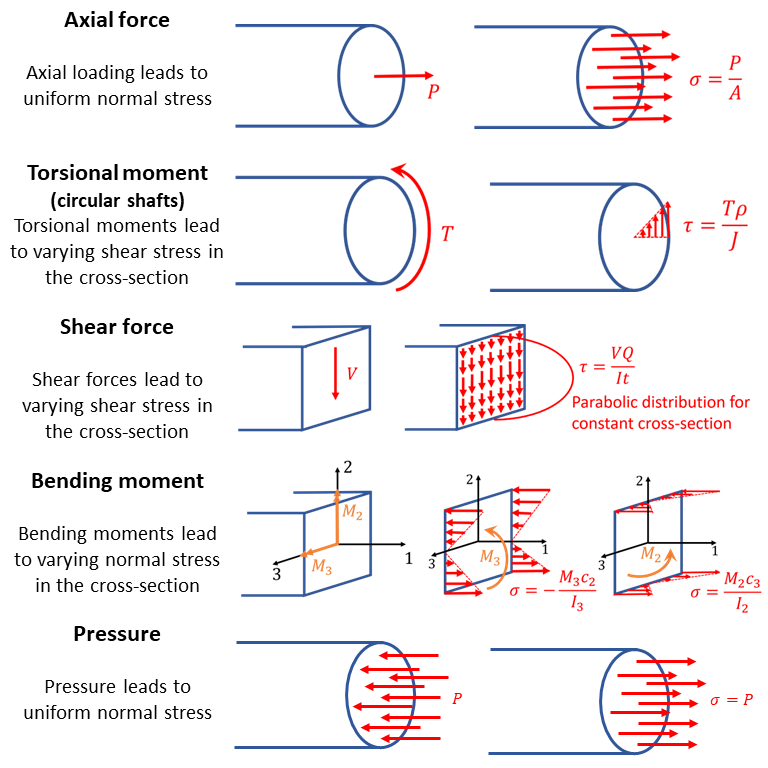
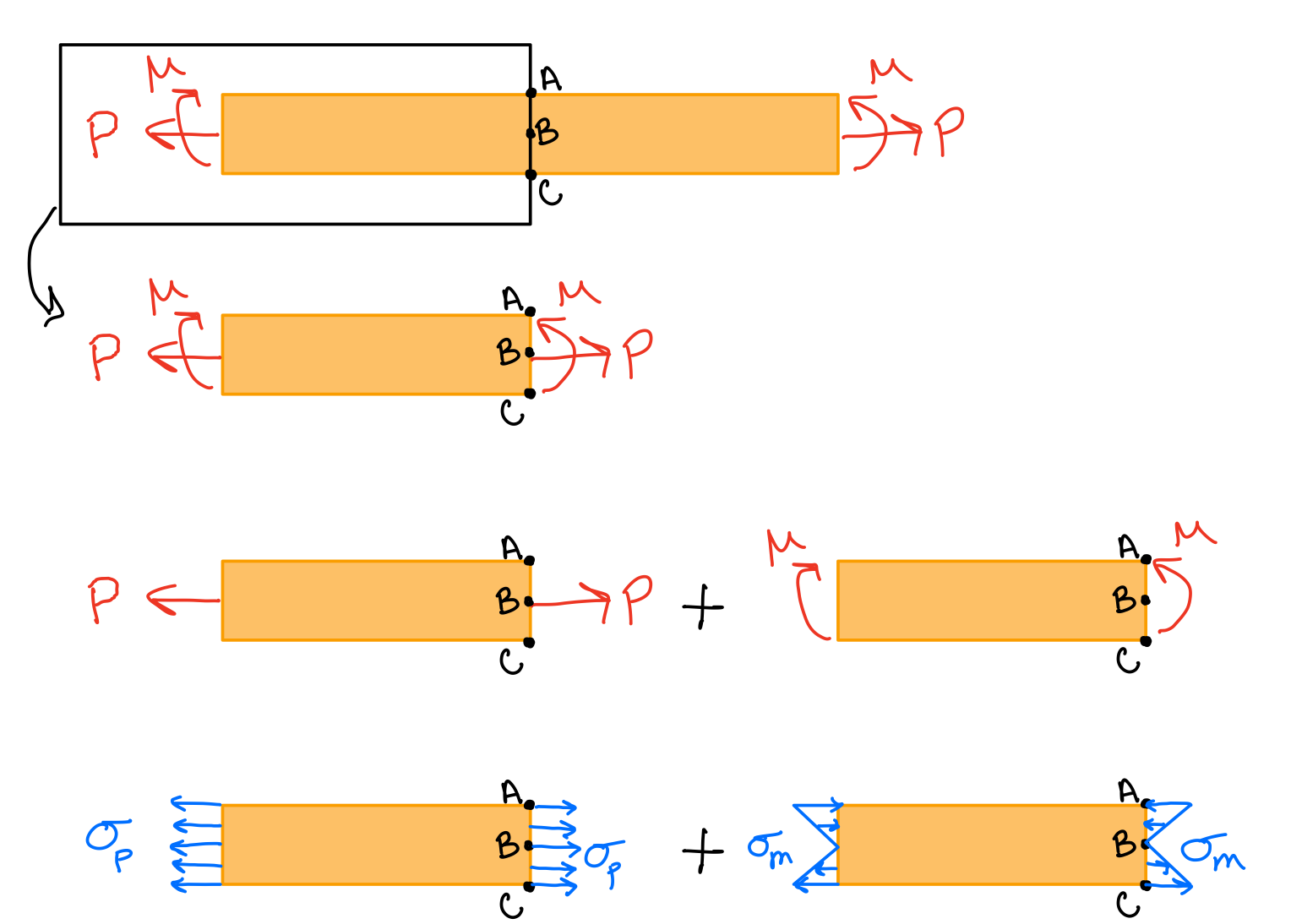
The goal in combined loading is to determine the stresses at a point in a slender structural member subjected to arbitrary loadings. A cross-section is cut through the point of interest and the internal loading/moments are evaluated at the centroid of the section to maintain equilibrium. This internal system of loading will consist of three force components and three couple vectors (moments). To determine the stress distribution at the point, the principle of superposition is applied.
Steps: - Cut the beam to find the find internal forces/moments in a section of interest.
- Calculate all the stresses acting at a specific point within that section.
- Add up like stresses (matching subscripts) to find the total stress state (superposition).
Combined Loading Summary: - Axial force and in-plane couple vectors (moments) contribute to the normal stress distribution in the section.
- Shear forces and the twisting couple vector (moment) contribute to the shear stress distribution in the section.